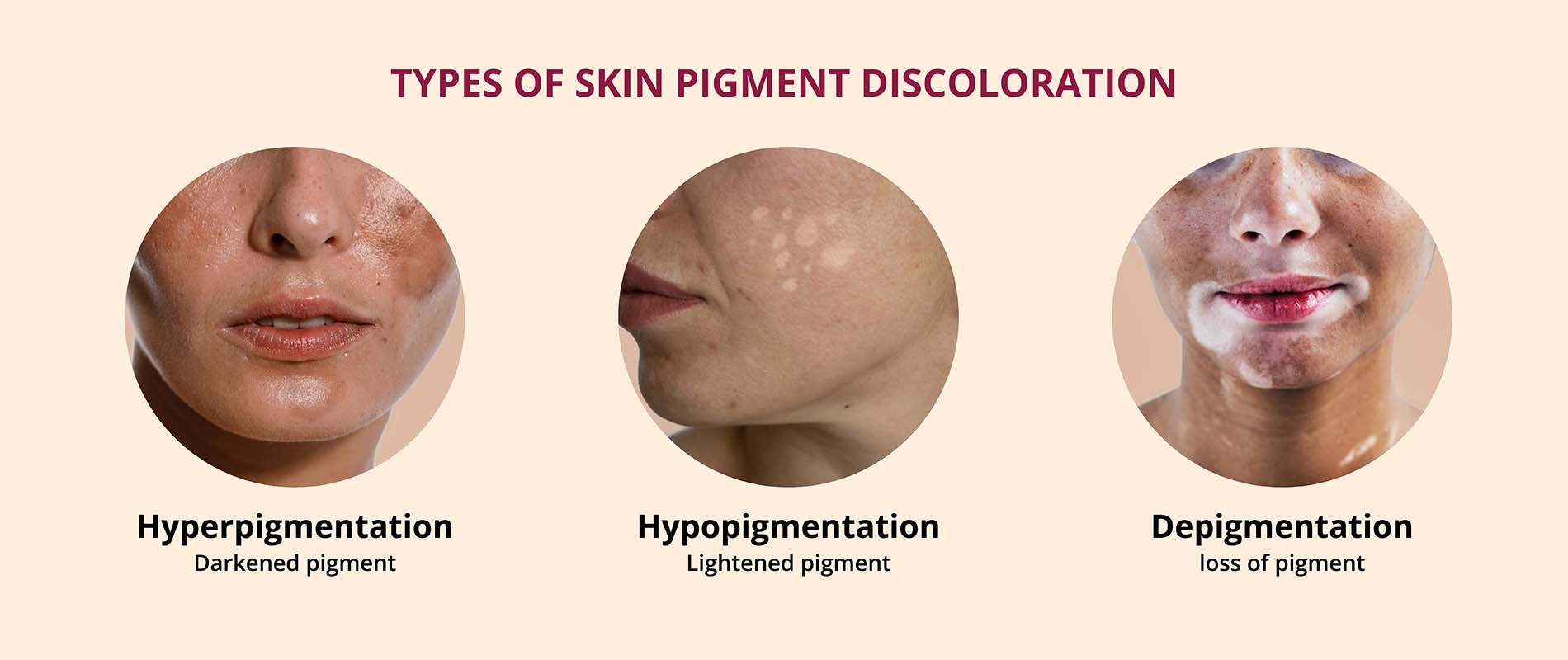
Hypopigmentation
Skin CareOverview
What is hypopigmentation?
Hypopigmentation is a low amount of Melanin in your skin. Patches of your skin are lighter in color than your surrounding skin.
Your skin, hair and eyes get their color from a chemical called melanin. When your skin cells don’t make enough melanin, areas of your skin become lighter.
 Causes
Causes
What causes hypopigmentation?
Injuries to your skin are the most common cause of hypopigmentation, including:
- Burns.
- Infections.
- Blisters.
- Chemical exposure.
As these injuries heal, scars may develop that are lighter than your surrounding skin.
Rare genetic conditions may cause hypopigmentation over wide areas of your skin. Some of these genetic conditions include:
Albinism
Albinism is an inherited disorder that results from a change in one of the genes that affect melanin production. The result is a reduction in melanin and a lack of skin pigmentation. Albinism is present from birth but does not become more severe over time.
A person with albinism may have:
- very pale skin
- hair that is white, very blond, brown, or reddish
- light-colored irises in the eyes
The person may also have eyesight problems, as melanin plays a role in the development of the retina, a part of the eye that plays an essential role in vision. They will also be more prone to sunburn and skin cancer.
Vitiligo

Vitiligo is a long-term condition in which pale patches appear on the skin.
It can affect any part of the body but most commonly occurs on the
- face, especially the eyes and mouth
- inside of the mouth
- neck
- hands, particularly the fingers and wrists
- groin and genital area
- armpits
Pityriasis alba
A person with pityriasis alba will have raised, slightly inflamed patches on their skin that can lose pigment over time. The lesions usually resolve within a yearTrusted Source without intervention. However, it can take several months to a few years for the pigmentation to return.
Pityriasis alba tends to be more noticeable in people with darker skin
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pityriasis-alba-5-d6969da7f5ec4c6f971b11d4122c100c.jpg)
The lesions usually affect the:
- face
- arms
- upper trunk
The cause of pityriasis alba is not known, but it may be associated with atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema. The loss of pigmentation is probably a result of inflammation.
Pityriasis alba usually occurs during childhood and adolescence.
Pityriasis versicolor
 Pityriasis versicolor is a fungal skin infection, sometimes called tinea versicolor. The fungus that causes it lives on the skin of most people, but it does not usually cause symptoms and is not contagious.
Pityriasis versicolor is a fungal skin infection, sometimes called tinea versicolor. The fungus that causes it lives on the skin of most people, but it does not usually cause symptoms and is not contagious.However, if the fungus grows more than usual, the skin can change color in patches,
usually on the:
- ches
- upper back
- abdomen
- upper arms
On darker skin, the patches are often light. On pale skin, they may be pink, red, or pale brown. They are flat and circular and can join together to for’
Other hypopigmentation causes include:
- Lichen sclerosus is a disorder that affects the skin on your genitals or anus.
- Psoriasis is a long-lasting (chronic) disorder that causes thick, scaly patches (plaques) on your skin. Hypopigmentation may appear once your plaques go away.
- Eczema is a condition that causes your skin to become dry, discolored, itchy and bumpy. After treatment, your affected areas may have hypopigmentation.
Some skin treatments may also cause hypopigmentation, including:
- laser skin resurfing . During this procedure, your healthcare provider uses lasers to remove skin irregularities from the top layers of your skin. Skin irregularities may include sun damage, wrinkles, acne scars and age spots. Laser skin resurfacing stimulates the growth of new collagen fibers, which results in new, smoother skin. Hypopigmentation may result in your treated areas.
- Laser hair removal uses heat from a laser to destroy your hair follicles. The heat may damage your surrounding skin and cause hypopigmentation.
- Dermabrasion . During this procedure, a dermatologist or plastic surgeon scrapes away irregularities in the top layers of your skin. If you have skin of color, you’re more likely to have hypopigmentation after dermabrasion
- . Chemical peels improve irregularities in your skin. A chemical solution causes the top layers of your skin to peel off, resulting in smoother, brighter skin. If you have skin of color, you have a greater risk of experiencing hypopigmentation after treatment that targets deeper layers of your skin (post-inflammatory hypopigmentation).
Care and Treatment
How is hypopigmentation treated?
Treatment for hypopigmentation depends on the cause.
- Albinism: This does not need treatment, but a person should take care to protect their skin and eyes from UV rays.
- Vitiligo: No treatment is necessary, but short-term use of steroid creams or light treatment may help restore some color temporarily. Camouflage makeup can also help mask the patches.
- Pityriasis alba: Low-dose steroid creams may help reduceTrusted Source inflammation and speed up repigmentation. Other options for people with more extensive cases include psoralen plus UVA (PUVA) photochemotherapy and targeted phototherapy.
- Pityriasis versicolor: Antifungal treatments, such as creams, shampoos, or tablets can help manage the infection.
If you have hypopigmentation from injuries to your skin or skin treatment, you likely won’t need treatment. Your skin cells will start to make melanin again as your affected areas heal. Hypopigmentation will usually go away after a few weeks or months.
If you have pityriasis alba, psoriasis or eczema, hypopigmentation usually goes away on its own without treatment. It may take a few weeks or months.
If hypopigmentation is a symptom of a skin condition, certain medications can treat it. These medications may include corticosteroids and topical calcineurin inhibitors, including tacrolimus ointment and pimecrolimus cream.
Phototherapyis effective if you have hypopigmentation from laser treatments (laser-induced hypopigmentation). These treatments include laser hair removal, laser tattoo removal or laser skin resurfacing. It uses ultraviolet (UV) light from special lamps. Your healthcare provider may use a drug called psoralen combined with ultraviolet A (PUVA) or ultraviolet B (UVB). Studies suggest that phototherapy helps treat laser-induced hypopigmentation in skin of color.
There aren’t any effective treatments for albinism or scars that have hypopigmentation.
Is hypopigmentation permanent?
It depends on what’s causing your hypopigmentation.
If you have albinism or hypopigmentation from scars, it’s permanent.
Hypopigmentation from injuries, treatments and certain skin conditions may go away on its own or go away after treatment.
What can I do at home to treat hypopigmentation?
Certain home remedies may help improve the appearance of your hypopigmentation. These may include:
- Cosmetics. Makeup, self-tanner or skin dye help make hypopigmentation less visible.
- Sunscreen. The sun can be especially damaging to areas of your skin with hypopigmentation. Use sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 to help protect your affected areas.
Home remedies are safe for most people. However, it’s a good idea to check with your healthcare provider before trying some of these options.
Does vitamin C help hypopigmentation?
Some people believe that vitamin C may help hypopigmentation in damaged skin. Vitamin C helps protect the cells in your body and helps form collagen. Collagen gives structure, strength and elasticity to your skin.
You may take vitamin C as an oral supplement, or you may apply it directly onto your skin. Vitamin C lotions or creams make your skin more sensitive to the sun, so use sunscreen on a daily basis while using a product that contains vitamin C.
When To Call the Doctor
When should hypopigmentation be treated by a healthcare provider?
You’re at a greater risk of developing skin cancer if you have albinism. Your healthcare provider can tell you the best ways to protect and take care of your skin.
See your healthcare provider if you have lichen sclerosus. Having lichen sclerosus increases your chances of developing a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Hypopigmentation can also affect your mental health. It can make you worry about how others look at you. It can also affect how you think about yourself and your behavior. If hypopigmentation causes you stress, anxiety or depression, see your healthcare provider right away.
Additional Common Questions
Can microneedling treat hypopigmentation?
Microneedling may be able to treat hypopigmentation. However, there isn’t enough research to say for sure.
During microneedling, your healthcare provider uses a device that pokes your skin with thin needles. The tiny punctures in your skin stimulate the growth of new collagen and elastin fibers. They may also stimulate your skin cells to make more pigment.
What’s the difference between hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation makes some areas of your skin darker than others. Damaged or unhealthy skin cells produce too much melanin. The melanin can clump, causing that area to appear darker.
What’s the difference between hypopigmentation and vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a disorder that causes your skin to lose its color. Hypopigmentation is a symptom of vitiligo.

